- Packet Tracer Command Prompt Ping
- Packet Tracer Command Line
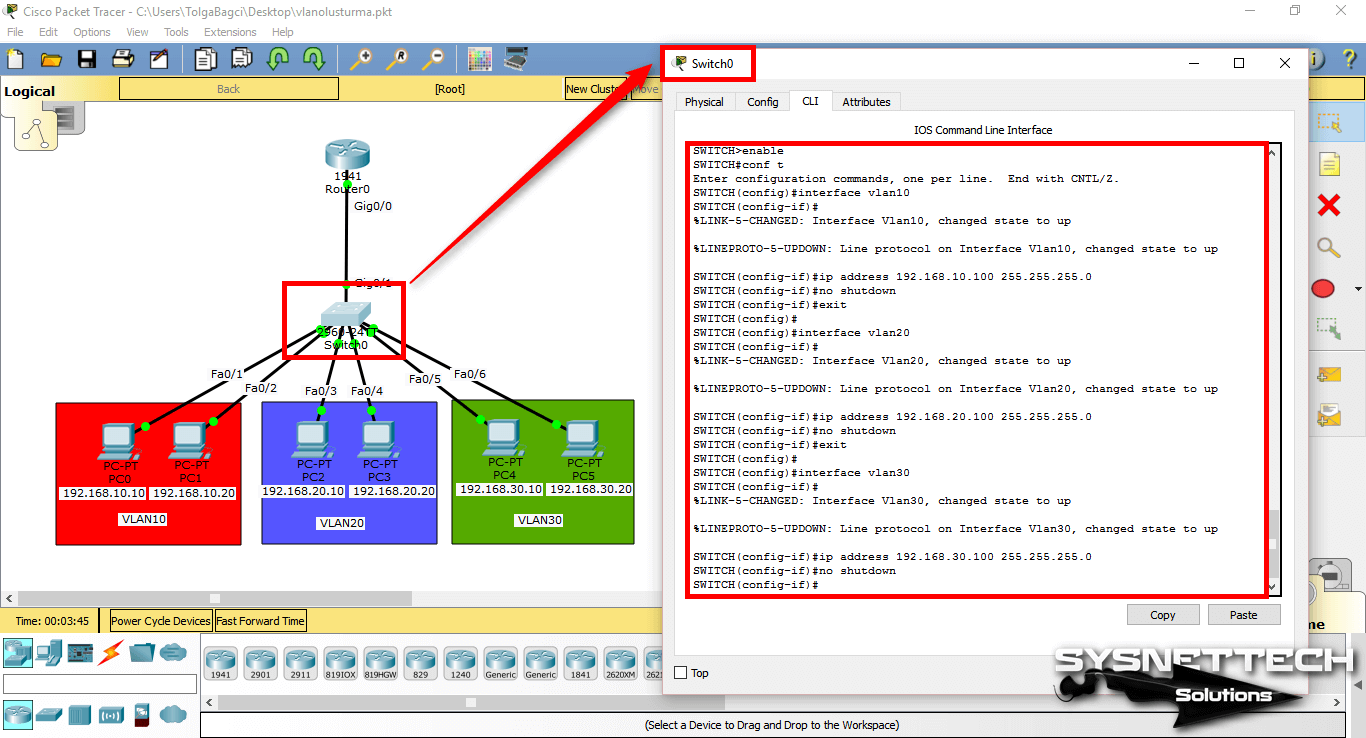
- Packet Tracer Router Commands
- Clear Command Prompt Packet Tracer
9.2.3.3 Packet Tracer – Using the Ping Command Answers
Packet Tracer – Using the Ping Command (Answers Version)
There's an easy way to fix that - line the line section of the config, enter the command 'logging synchronous' i.e. This will force notifications to appear on a new line and not mess up your terminal. Cisco Packet Tracer vs Emulators. Step 6: The second way to enter a static IP address is through CLI, this is the most efficient way to program the computers in CISCO PACKET TRACER because it is the most accurate way of working in real equipment. To do this, enter the global user mode and place the following commands: Interface fastethernet 0/0. Ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0.
Lists a single line of information about each interface, including the IP address, line and protocol status, and the method with which the address was configured (manual or DHCP). Ipconfig /all Enables the MAC address information to be displayed from the command prompt, shows address if DNS server.
Answers Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the Answers copy only.
Topology
Objectives
Use the ping command to identify an incorrect configuration on a PC.
Background / Scenario
A small business owner learns that some users are unable to access a website. All PCs are configured with static IP addressing. Use the ping command to identify the issue.
Packet Tracer Command Prompt Ping
Step 1: Verify connectivity.
Access the Desktop tab > Web Browser of each PC and enter the URL www.cisco.pka. Identify any PCs that are not connecting to the web server.
Packet Tracer Command Line
Note: All of the devices require time to complete the boot process. Please allow up to one minute before receiving a web response.
Which PCs are unable to connect to the web server?_____________ PC2
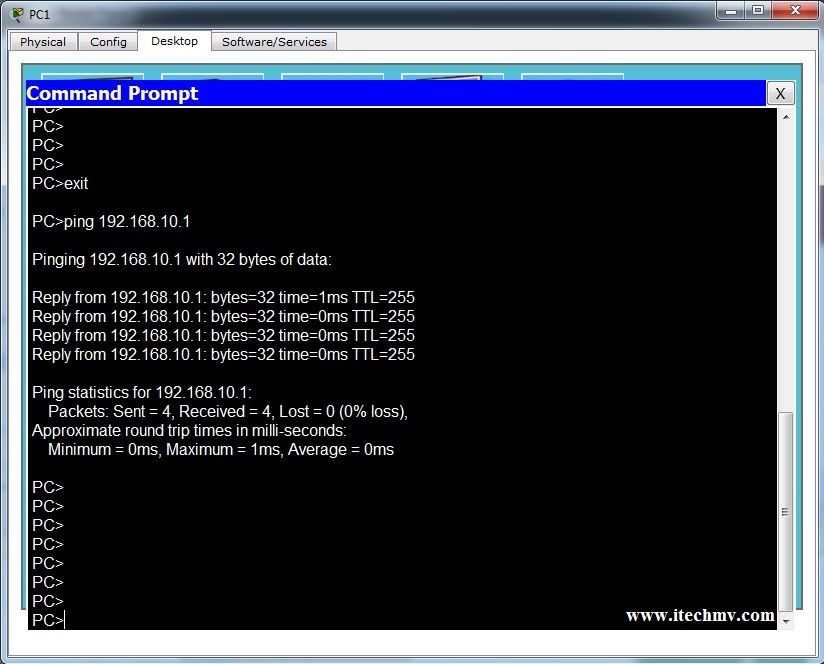
Step 2: Ping the web server from PC2.
- On PC2, access the Command Prompt from the Desktop tab.
- Type ping www.cisco.pka.
Did the ping return a reply? What is the IP address displayed in the reply, if any?____________________________________________________________________________________
There was no reply. No IP address was displayed in the message.
Step 3: Ping the web server from PC1.
Packet Tracer Router Commands
- On PC1, access the Command Prompt from the Desktop tab.
- Type ping www.cisco.pka.
- Did the ping return a reply? What is the IP address returned, if any?____________________________________________________________________________________
Reply was returned with 192.15.2.10 as the IP address for www.cisco.pka.
Step 4: Ping the IP address of the web server from PC2.
- On PC2, access the Command Prompt from the Desktop tab.
- Attempt to reach the IP address of the web server with the command ping 192.15.2.10.
- Did the ping return a reply? If so, then PC2 is able to reach the web server via IP address, but not domain name. This could indicate a problem with the DNS server configuration on PC2.
Step 5: Compare the DNS server information on PC2 with other PCs on the local network.
- Access the Command Prompt of PC1.
- Using the command ipconfig /all, examine the DNS server configuration on PC1.
- Access the Command Prompt of PC2.
- Using the command ipconfig /all, examine the DNS server configuration on PC2. Do the two configurations match?
Step 6: Make any necessary configuration changes on PC2.
Clear Command Prompt Packet Tracer
- Navigate to the Desktop tab of PC2, make any necessary configuration changes in IP Configuration.
- Using the Web Browser within the Desktop tab, connect to www.cisco.pka to verify that the configuration changes resolved the problem.
- Click the Check Results button at the bottom of this instruction window to check your work.